Mapping data source fields
Analyze survey response data for similar questions across surveys in a single field, and create configurable dashboards and crosstab reports to aggregate data from multiple surveys.
When you add multiple primary data sources to a dataset, you can control how the data is stored and is available for analysis using data mapping. Data mapping allows you to map fields in an activity to one or more additional activities. For example, if you send members a monthly NPS®1 survey, you can add the activity for each monthly survey to your dataset and map the NPS® value field and any other common fields of interest. The resulting dataset will include one NPS® value field with the data for each activity appended vertically. Storing data in this format makes it suitable for performing time series analysis on the dataset in your dashboards. You can also create a crosstab report to analyze survey response data from similar questions across surveys as a single field.
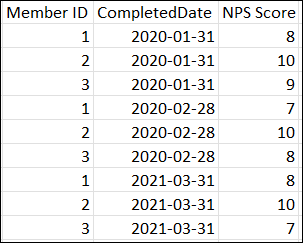
When you map fields, a row is created for each member ID from each activity in the dataset. If a member answers 12 consecutive NPS® surveys their responses will be recorded in 12 rows in the dataset.
You can combine up to 20 activities as data sources. Each data source must be added as a primary data source. Profile variables can be included in the same dataset as the data mappings, but profile variables cannot be mapped.
Any fields in your data sources that you choose not to map, and those that cannot be mapped, will be added horizontally as new columns to the dataset. If an activity has a field that is not found in any of the other data sources, a new column will be added to the dataset for that field. The column will only contain values for the field in the rows associated with the activity that has the field. The column will have null values for all other activities.
You cannot add data mapping to activities for datasets that have been synced without any data mapping applied. If you add data mappings to a dataset and sync it, you cannot change any of the existing mapped fields after syncing, but you can add additional data sources and map the new fields from those data sources.
Once you add a data mapping to your dataset you cannot add custom fields, scalar fields, or weighting to the dataset. You also cannot append external data to the dataset from a CSV file.
Automatically Mapping Fields
Supported fields in datasets are automatically mapped by default when a second primary data source is added to the dataset and the Apply Auto Mapping checkbox remains selected. The checkbox is selected by default.
Individual fields are automatically mapped when they meet the following criteria:
- The field types must be the same.
- The field names (the questions in the surveys) must be the same.
- If the field values (the answers in the surveys) include a fixed set of options, the number of values and the actual values must be the same.
Fields from the same source that are identical will not have auto mapping applied.
You can view and verify the automatically mapped fields for each data source in the Data Mapping tab using the Data Source drop-down list to switch between the data sources in the dataset.